使用JWT进行认证
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are a more modern approach to authentication.
As the web moves to a greater separation between the client and server, JWT provides a wonderful alternative to traditional cookie based authentication models.
JWTs provide a way for clients to authenticate every request without having to maintain a session or repeatedly pass login credentials to the server.
用户注册之后, 服务器生成一个 JWT token返回给浏览器, 浏览器向服务器请求数据时将 JWT token 发给服务器, 服务器用 signature 中定义的方式解码
JWT 获取用户信息.
一个 JWT token包含3部分:
1 header: 告诉我们使用的算法和 token 类型
2 Payload: 必须使用 sub key 来指定用户 ID, 还可以包括其他信息比如 email, username 等.
3 Signature: 用来保证 JWT 的真实性. 可以使用不同算法
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"strings"
"time"
"github.com/codegangsta/negroni"
"github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go"
"github.com/dgrijalva/jwt-go/request"
)
const (
SecretKey = "welcome ---------"
)
func fatal(err error) {
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}
type UserCredentials struct {
Username string `json:"username"`
Password string `json:"password"`
}
type User struct {
ID int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
Username string `json:"username"`
Password string `json:"password"`
}
type Response struct {
Data string `json:"data"`
}
type Token struct {
Token string `json:"token"`
}
func StartServer() {
http.HandleFunc("/login", LoginHandler)
http.Handle("/resource", negroni.New(
negroni.HandlerFunc(ValidateTokenMiddleware),
negroni.Wrap(http.HandlerFunc(ProtectedHandler)),
))
log.Println("Now listening...")
http.ListenAndServe(":8087", nil)
}
func main() {
StartServer()
}
func ProtectedHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
response := Response{"Gained access to protected resource"}
JsonResponse(response, w)
}
func LoginHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var user UserCredentials
err := json.NewDecoder(r.Body).Decode(&user)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
fmt.Fprint(w, "Error in request")
return
}
if strings.ToLower(user.Username) != "someone" {
if user.Password != "p@ssword" {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
fmt.Println("Error logging in")
fmt.Fprint(w, "Invalid credentials")
return
}
}
token := jwt.New(jwt.SigningMethodHS256)
claims := make(jwt.MapClaims)
claims["exp"] = time.Now().Add(time.Hour * time.Duration(1)).Unix()
claims["iat"] = time.Now().Unix()
token.Claims = claims
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error extracting the key")
fatal(err)
}
tokenString, err := token.SignedString([]byte(SecretKey))
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprintln(w, "Error while signing the token")
fatal(err)
}
response := Token{tokenString}
JsonResponse(response, w)
}
func ValidateTokenMiddleware(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, next http.HandlerFunc) {
token, err := request.ParseFromRequest(r, request.AuthorizationHeaderExtractor,
func(token *jwt.Token) (interface{}, error) {
return []byte(SecretKey), nil
})
if err == nil {
if token.Valid {
next(w, r)
} else {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
fmt.Fprint(w, "Token is not valid")
}
} else {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusUnauthorized)
fmt.Fprint(w, "Unauthorized access to this resource")
}
}
func JsonResponse(response interface{}, w http.ResponseWriter) {
json, err := json.Marshal(response)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.Write(json)
}
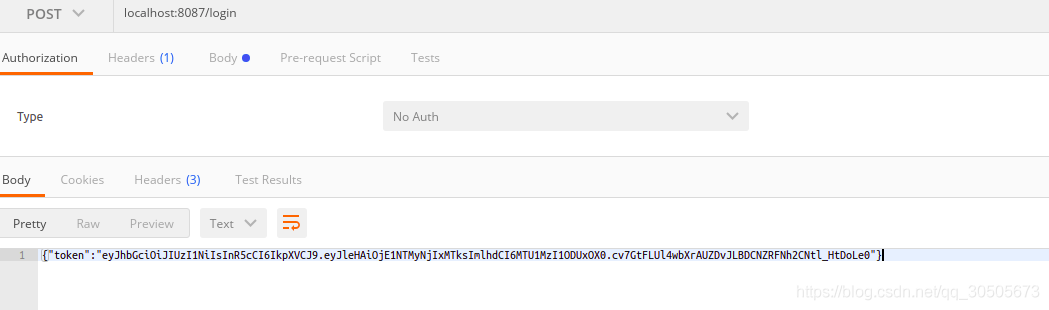
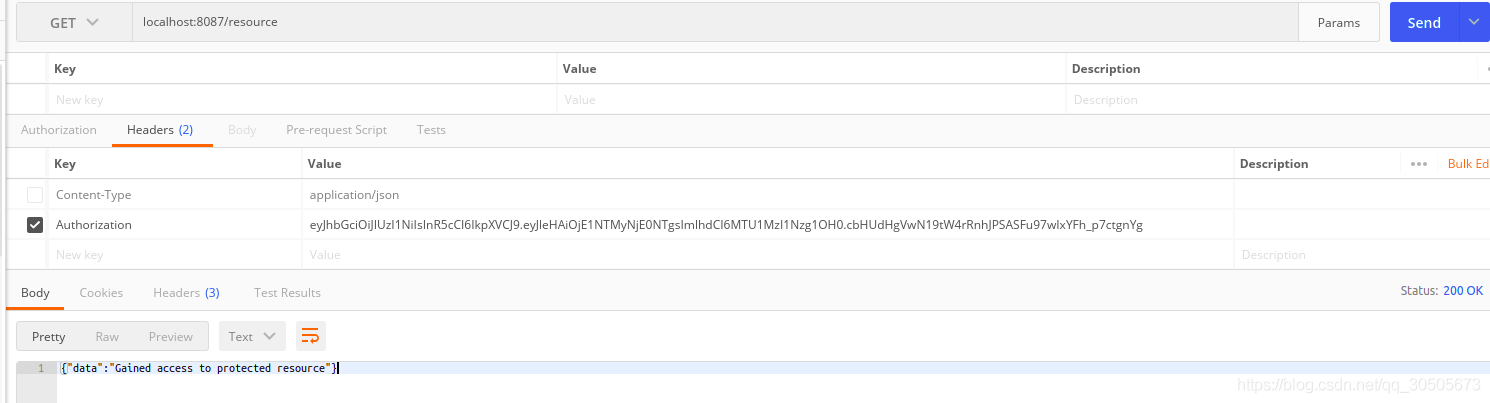
到此这篇关于golang进行简单权限认证的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Golang 权限认证内容请搜索M135模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持M135模板网!
0

